Betni Betamethasone Injection
$75.00 – $200.00Price range: $75.00 through $200.00
Betni Injection is used to reduce inflammation and treat allergic or autoimmune conditions. It contains Betamethasone, a corticosteroid that helps suppress the immune response, reducing swelling, redness, and irritation.
| Pack Size | Price | Price / Unit | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Injections | $75.00 | $15.00 / unit | ||
| 10 Injections | $120.00 | $12.00 / unit | ||
| 20 Injections | $200.00 | $10.00 / unit |
Looking for bulk / B2B pricing? | Send Inquiry |

| SKU | 11169 |
| Manufacturer | Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
| Categories | Inflammation |
| Delivery Time | 10 - 14 Working Days |
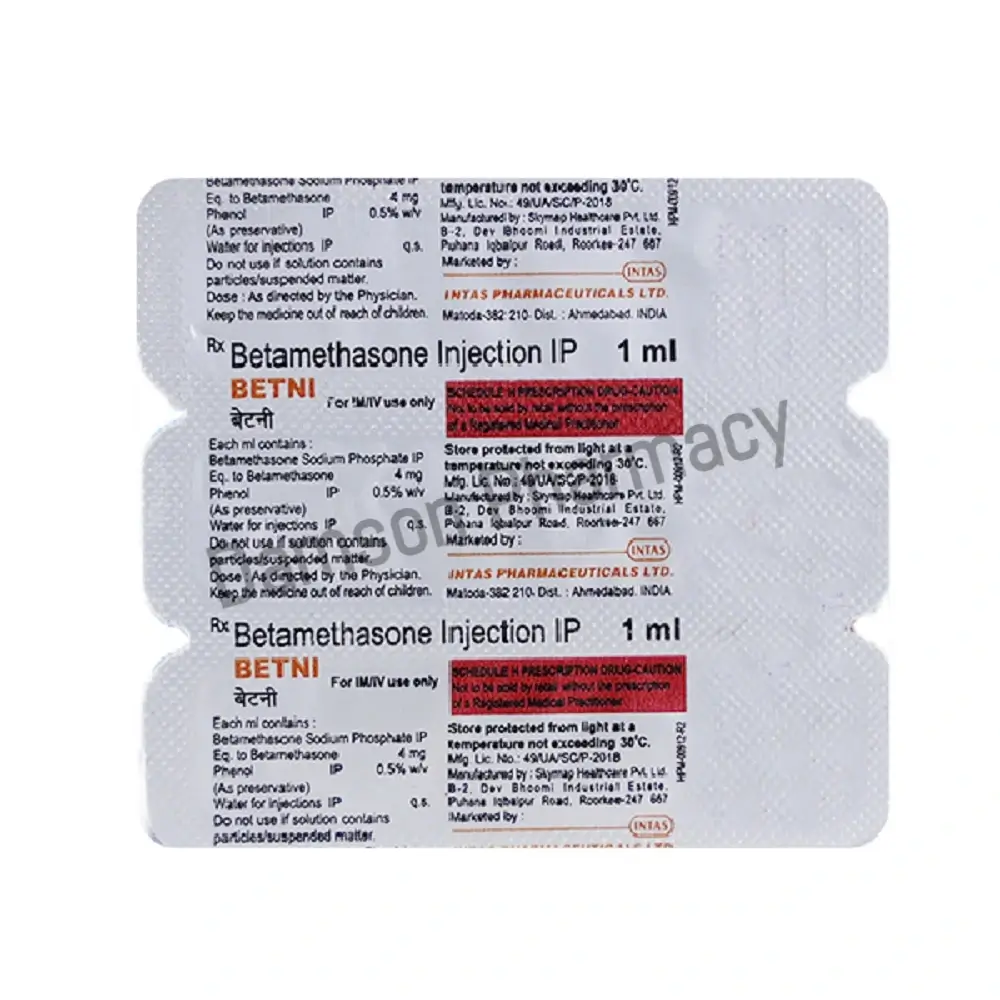
| Strength | 1ml |
Introduction to Betni Betamethasone Injection
Betni Betamethasone injection is a corticosteroid medication used to reduce inflammation and treat various conditions related to the immune system, skin, and other organs. It is manufactured by Intas Pharmaceuticals.
It works by suppressing the immune system’s inflammatory response, helping to manage conditions such as arthritis, allergies, skin disorders, and respiratory issues. Betni Betamethasone is also used to treat conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, certain types of cancer, and severe allergic reactions.
The injection is administered directly into the muscle or vein, and the dosage depends on the condition being treated and the patient’s individual response. It is often used when oral corticosteroids are not effective or suitable. Betamethasone is sometimes used for conditions involving swelling or inflammation, such as after surgery or trauma.
Uses of Betni Betamethasone Injection
Betamethasone injection is used for a variety of conditions, including:
- Inflammatory Disorders
- Allergic Reactions
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Respiratory Conditions
- Skin Conditions
- Endocrine Disorders
- Cancer Treatment
- Post-surgical Inflammation
How Does Betni Betamethasone Injection Works?
Betamethasone injection works by mimicking the effects of cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. It reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune system by inhibiting the release of substances that cause swelling, redness, and irritation.
This helps to control symptoms in conditions like arthritis, allergies, and autoimmune diseases. Betamethasone also affects metabolism, fluid balance, and immune responses, making it effective in treating a wide range of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders.
Side Effects of Betni Betamethasone
Common Side Effects
- Weight gain
- Increased blood sugar
- Mood changes
- Insomnia
- Stomach upset
- Weakening of bones
- Skin thinning
Serious Side Effects
- Severe allergic reactions
- Infections
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Psychiatric effects
Dosage of Betni Betamethasone Injection
The dosage of Betamethasone injection depends on the condition being treated and the patient’s individual response. Typically, the initial dose can range from 2 to 8 mg, administered once or divided into multiple doses per day, depending on the severity of the condition.
For more severe conditions, higher doses may be required. After the initial phase, the dose is gradually reduced to the lowest effective amount. The injection is given either intramuscularly or intravenously, and the treatment duration varies based on the specific disease and patient response.
How To Manage Side Effects of Betni Betamethasone Injection?
- Monitor weight
- Control blood sugar
- Eat a balanced diet
- Practice good sleep hygiene
- Take medications as prescribed
- Exercise regularly
- Monitor mood and mental health
Warnings & Precautions
Betni Betamethasone injections come with specific warnings and precautions that individuals and healthcare providers should be aware of. These warnings and precautions are important to ensure the safe and effective use of the medication. It’s crucial to discuss these aspects with a healthcare professional before starting betamethasone injections. Here are some important warnings and precautions associated with Betni betamethasone injections:
1. Adrenal Suppression:
- Prolonged use of betamethasone can suppress the adrenal glands, leading to adrenal insufficiency. Abruptly stopping the medication can result in adrenal crisis. Patients should be monitored, and dosage reduction should be gradual under medical supervision.
2. Immunosuppression:
- Betamethasone’s immunosuppressive effects can increase susceptibility to infections. Patients should be monitored for signs of infection, and the use of live vaccines should be avoided during treatment.
3. Hyperglycemia:
- Betamethasone can elevate blood glucose levels. Close monitoring is essential for individuals with diabetes, and adjustments to diabetes medications may be necessary.
4. Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance:
- Betamethasone can cause fluid retention and electrolyte imbalances. Patients with heart failure or hypertension should be closely monitored, and sodium and potassium intake may need adjustment.
5. Psychiatric Effects:
- Corticosteroids, including betamethasone, may cause mood swings, irritability, or psychiatric symptoms. Individuals with a history of psychiatric disorders should be closely monitored.
6. Osteoporosis:
- Long-term use of betamethasone is associated with decreased bone density and an increased risk of osteoporosis. Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, along with weight-bearing exercise, should be encouraged.
Storage
- Store at room temperature
- Protect from light
- Avoid freezing
- Keep away from heat and moisture
- Keep out of reach of children
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I receive Betni betamethasone injections at home?
Betamethasone injections are usually administered in a clinical setting by healthcare professionals. Self-administration at home is not typical, and individuals should not attempt to inject themselves without proper training.
2. How often can Betni betamethasone injections be given?
The frequency of betamethasone injections depends on the medical condition being treated. In some cases, a single injection may be sufficient, while in others, a series of injections may be prescribed. The healthcare provider will determine the appropriate schedule.
3. What precautions should I take during Betni betamethasone treatment?
Patients should follow the prescribed dosage and schedule, report any side effects to their healthcare provider, attend regular follow-up appointments, and be aware of precautions related to bone health, diabetes, and adrenal suppression.
4. Can Betni betamethasone injections be used during pregnancy?
The use of betamethasone during pregnancy should be carefully considered. The potential benefits must be weighed against the potential risks. It is essential to discuss this with the healthcare provider.
| Pack Size | 10 Injections, 20 Injections, 5 Injections |
|---|---|
| Price/Unit | $10/unit, $12/unit, $15/unit |
4 reviews for Betni Betamethasone Injection
Add a review Cancel reply
Related Products
No related Products Found





James –
Brilliant support and service when there was an issue with payment system
Harly –
Excellent customer service. I messaged with a question, and they replied to the next working day. Great service and communication.
Sam Carl –
Super efficient and simple!
Vitaly –
Good Services